How to use entity callbacks
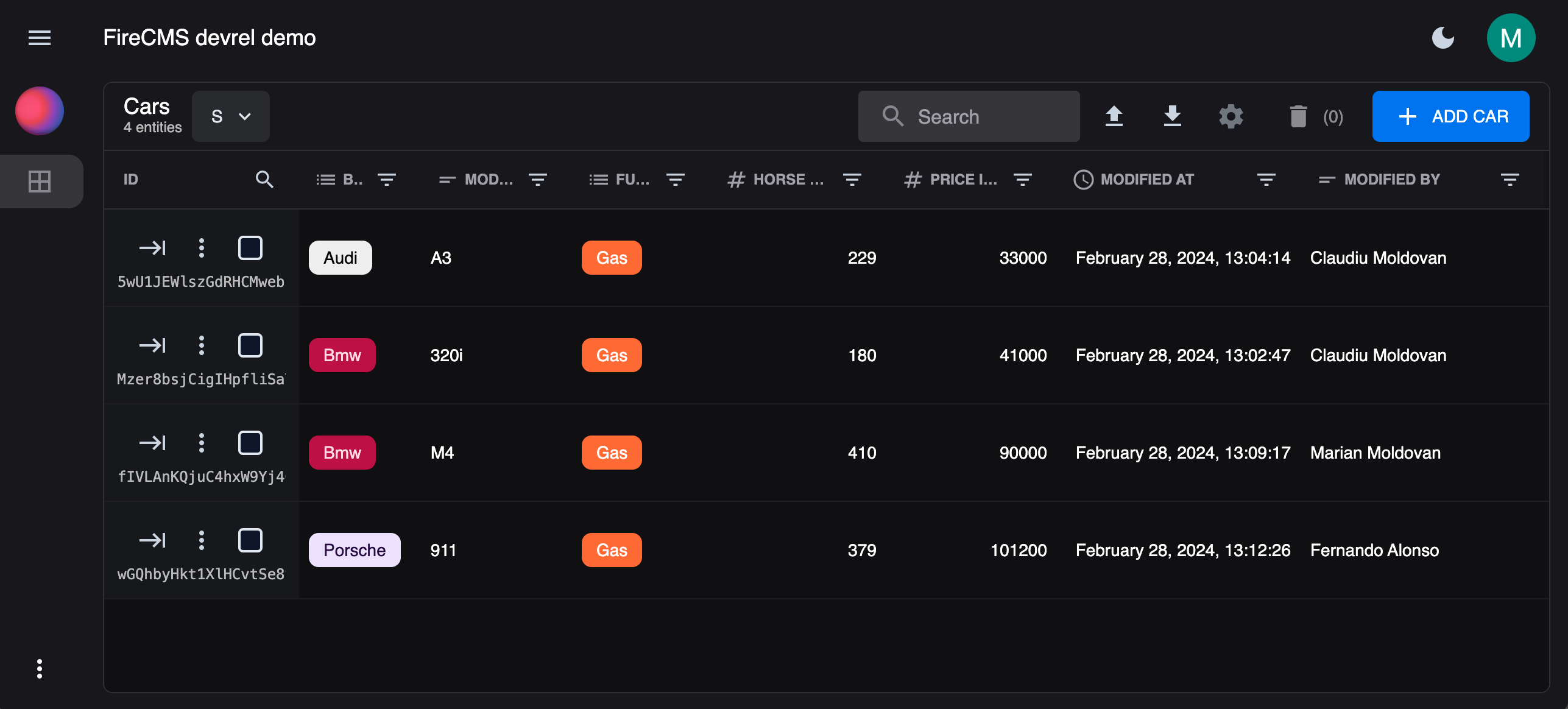
In this tutorial we will create a simple collection, containing cars. Then, we are going to use the Entity Callbacks to can track changes in the entity, adding the timestamp of the last update and the user who made the change.
What are entity callbacks?
Section titled “What are entity callbacks?”Entity callbacks are functions that are triggered at different stages of an entity’s lifecycle in a database. They are particularly useful for:
- Data Validation: They can be used to validate data before it is saved to the database. This can help ensure that the data meets certain criteria or conforms to certain formats.
- Data Transformation: They can be used to transform data before it is saved or after it is fetched from the database. This can be useful for tasks like converting data types, formatting data, or adding additional fields.
- Tracking Changes: They can be used to track changes to entities. For example, they can be used to add metadata to an entity, such as the timestamp of the last update and the user who made the change.
- Implementing Custom Logic: They can be used to implement custom logic rules. For example, they can be used to prevent certain actions, like deleting entities that the user didn’t create. You can use the auth modules and roles to define any logic.
- Auditing: They can be used to maintain an audit trail of changes made to the data. This can be useful for debugging and for maintaining data integrity.
In FireCMS we have been using these features in all versions, and it’s also available in version 3.0.
Create a collection
Section titled “Create a collection”For illustrative purposes, let’s create a simple cars collection.
The interface of the collection will look like this:
interface Car { brand_name: string; model_name: string; fuel_type: "diesel" | "gas"; horse_power: number; price_in_dollars: number; modified_at?: Date; modified_by?: string;}And the collection configuration will look like this:
export const carsCollection = buildCollection<Car>({ id: "cars", name: "Cars", path: "car", callbacks: carsCallbacks, singularName: "Car", properties: { brand_name: buildProperty({ dataType: "string", name: "Brand Name", validation: { required: true }, enumValues: [ { id: "alfa-romero", label: "Alfa Romero" }, { id: "audi", label: "Audi" }, { id: "bmw", label: "Bmw" }, { label: "Mercedes Benz", id: "mercedes-benz" }, { id: "porsche", label: "Porsche" } ] }), model_name: buildProperty({ dataType: "string", name: "Model Name", validation: { required: true } }), fuel_type: buildProperty({ validation: { required: true }, dataType: "string", enumValues: [ { label: "Diesel", id: "diesel" }, { id: "gas", label: "Gas" }, { id: "electric", label: "Electric" } ], name: "Fuel type" }), horse_power: buildProperty({ validation: { required: true }, name: "Horse Power", dataType: "number" }), price_in_dollars: buildProperty({ dataType: "number", validation: { required: true }, name: "Price in Dollars" }), modified_at: buildProperty({ dataType: "date", name: "Modified At", validation: { required: false }, readOnly: true }), modified_by: buildProperty({ dataType: "string", name: "Modified By", validation: { required: false }, readOnly: true }) }});Simple enough, right? Now let’s add the callbacks.
Create the entity callbacks
Section titled “Create the entity callbacks”Now, you can check the interface of the EntityCallbacks in the documentation. We have all this callbacks available:
onFetch: Called when an entity is fetched from the database.onPreSave: Called before an entity is saved to the database.onSaveSuccess: Called after an entity is saved successfully to the database.onSaveFailure: Called when an error occurs while saving an entity to the database.onPreDelete: Called before an entity is deleted from the database.onDelete: Called when an entity is deleted successfully from the database.onIdUpdate: Callback fired when any value in the form changes. You can use it to define the ID of the entity based on the current values
We want to save the user who made the last change and the date of the last change. We can use the onPreSave callback to achieve this. We are going use the builder util function buildEntityCallbacks to create the callbacks. This is helpful for creating the callbacks for a specific entity type. So we have the types inside the functions.
const carsCallbacks = buildEntityCallbacks<Car>({ onPreSave: (entitySaveProps) => { console.log("Callback onPreSave<Car>"); // We set the modified_at with the current timestamp entitySaveProps.values.modified_at = new Date(); // We set the modified_by with the user who made the change using the displayName from the logged in user entitySaveProps.values.modified_by = entitySaveProps.context.authController.user?.displayName ?? "Unknown User"; // We need to return the values return entitySaveProps.values; }});As you can see by the code, we are using a new Date to get the current date and time, and we are using the authController to get the user who is making the change. If the user is not logged in, we are going to use the string “Unknown User” as the user who made the change.
And then, we just need to update the collection config to include the callbacks:
export const carsCollection = buildCollection<Car>({ id: "cars", name: "Cars", path: "car", callbacks: carsCallbacks, singularName: "Car", properties: { // ... properties }});Now, when we save the entity, the modified_at and modified_by fields will be updated with the current date and the user who made the change.

Now let’s implement another feature, let’s block deleting the cars, or entities that you haven’t created yourself; for that, we are gonna use the onPreDelete callback.
const carsCallbacks = buildEntityCallbacks<Car>({ onPreDelete: (entityDeleteProps) => { console.log("Callback onPreDelete<Car>"); if (entityDeleteProps.context.authController.user?.displayName !== entityDeleteProps.entity.modified_by) { throw new Error("You cannot a car that wasn't created by yourself"); } }});Now, when a user tries to delete a car that wasn’t created by themselves, an error will be thrown.
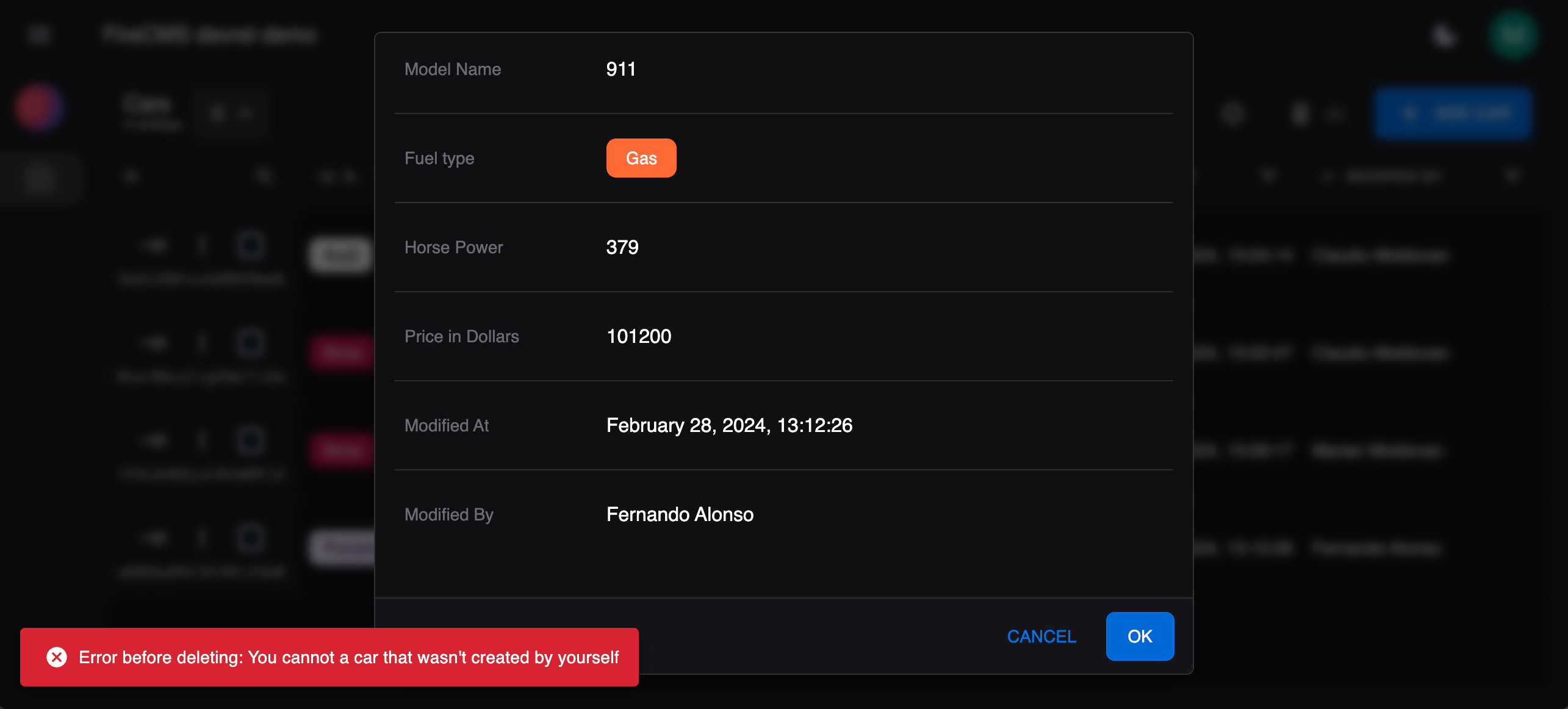
So, we cannot delete the cars that we didn’t create. In this example, the one created by the F1 driver Fernando Alonso.
Full code
Section titled “Full code”Full code available in the FireCMS repository

